- in Uncategorized by Tara Maya
How to Use Reiteration in Romance


Staurt Horwitz in his book Book Architecture makes the case for using Reiterations to create structure for a novel without tying yourself to a linear outline. Especially if you’re writing a literary book, a book with multiple viewpoint characters or multiple timelines, this method is gold.
Horwitz is weak on one point where Coyne is strong, however: Genre specific advice.
But how about if one combined Coyne’s and Horwitz’s methods?
I’m going to take my list of Obligatory Scenes for Romance, inspired by Coyne, and mash it up with Horwitz’s Reiteration method. Let’s see what happens!
First, here’s a re-cap of Obligatory Scenes for Romance.
- The Cute Meet: Meeting the each other is an unusual, even life-changing event, or occurs during some life-changing event. (If they knew each other long ago, this is replaced by an Unexpected Reunion. Sometimes, the Cute Meet is included too, as a prologue or a flashback.)
- The External Problem: Something outside the heroine and hero keeps them apart.
- The Internal Problem: Some internal wound keeps the heroine and hero apart.
- The Draw: Despite the problems, something forces the heroine and hero to spend time together.
- The First Kiss: The heroine and hero express their attraction for the first time.
- The First Fight: The heroine and hero quarrel, but overcome their difficulty.
- The Commitment: The heroine and hero admit to loving one another or in some way commit to one another.
- The Betrayal: Despite their commitment, either the external force or internal force keeping the lover apart threatens to separate them forever. There seems to be no way to overcome this.
- Love Conquers All: The heroine and hero overcome the betrayal, proving the strength of their commitment (even, in a tragedy like Romeo and Juliet, or a romance without a HEA like The Titanic or The Notebook) despite death). In other almost-romances, or romances involving very young teens, an ambiguous “happily ever after for now” is acceptable.
- The Happily Ever After (HEA): In a true sits-on-the-romance-shelf genre Romance, as opposed to a strongly romantic story that might end tragically, the hero and heroine remain in love, remain together, and remain alive: they live happily ever after. Their HEA may be confirmed in an epilogue, or whenever the couple shows up in later books (about other couples) of the same series.
First of all, notice Points 9 and 10. The larger Theme, and the outcome that proves that Theme, for all Genre Romance (as opposed to Women’s Fiction or literary novels with a love story) must be “Love Conquers All” and a Happily Ever After (HEA). This is part of the Genre. If you don’t like it, don’t write Genre Romance. That’s pretty simple.
That doesn’t let you off the hook from developing your own Theme, however. This will be a variation of Love Conquers All, a specific example of what kind of problem Love Conquers. For instance, in 50 Shades of Grey it would be: Love is stronger than sexual sadism. The theme of Pride and Prejudice would be: Love is stronger than social prejudice. Another book might have the theme: Love is stronger than greed. One of my favorites is the HEA version of Romeo and Juliet: Love is stronger than enmity.
So far, that’s just Romance 101.
Here’s where it gets interesting. In my list of Obligatory Scenes, there were three that bugged me, the scenes I labeled 2-4 on the list: the External Problem, the Internal Problem, and the Draw. They weren’t quite right—because they weren’t Obligatory Scenes, as such, but rather ongoing elements necessary to drive the Romance. These elements might go into every scene, in fact!
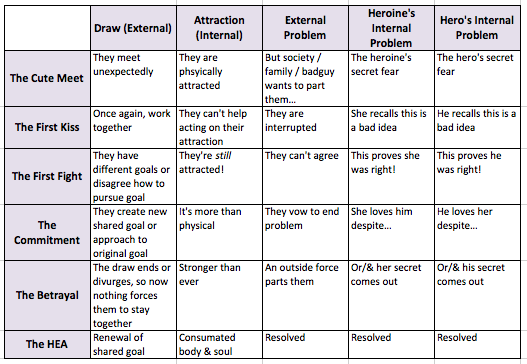
I was trying to use a linear sequence, but what I needed was a set of parallel sequences—a grid. First let’s leave only the real scenes in our list:
- The Cute Meet: Meeting the each other is an unusual, even life-changing event, or occurs during some life-changing event. (If they knew each other long ago, this is replaced by an Unexpected Reunion. Sometimes, the Cute Meet is included too, as a prologue or a flashback.)
- The First Kiss: The heroine and hero express their attraction for the first time.
- The First Fight: The heroine and hero quarrel, but overcome their difficulty.
- The Commitment: The heroine and hero admit to loving one another or in some way commit to one another.
- The Betrayal: Despite their commitment, either the external force or internal force keeping the lover apart threatens to separate them forever. There seems to be no way to overcome this.
- The Happily Ever After (HEA): In a true sits-on-the-romance-shelf genre Romance, as opposed to a strongly romantic story that might end tragically, the hero and heroine remain in love, remain together, and remain alive: they live happily ever after. Their HEA may be confirmed in an epilogue, or whenever the couple shows up in later books (about other couples) of the same series.
What happened to 2-4 and 9? They are still there, but along a different axis. Let’s look again at that list once we’ve turned it into a Reiteration Grid:
The Grid allows us to see that Reiterations can (potentially) iterate in every scene. (They don’t have to but they could.) This is critical, because touching on these narrative events is key to making a romance romantic. Each Obligatory Scene, as well as the other scenes in the book, will combine more than one Reiteration Arc.
Let’s take the Cute Meet. Looking at the Grid, we can see a there are several elements that might go into that scene. First there’s an iteration of Draw—the reason they are meeting and will continue to meet. Instantly, they are attracted to one another, though at this point it might be purely physical attraction. There may be an iteration of the External problem already evident. And even at this point, we should see the first iteration of the Heroine’s secret and the Hero’s secret, though the hint might be so well disguised we don’t recognize it as the first iteration of that Reiteration Arc until we’ve seen further iterations.
Least it seem the Grid is too, dare I say it, formulaic, let me emphasize that each individual story will have a different palette of Reiterations flowing into scenes. The Heroine and Hero might meet for the first time before they know that something is going to continue to work together, so there may be no Draw iteration in Cute Meet. Or they may meet, be attracted and go right to the First Kiss scene before an External antagonist pulls them away and stirs up the doubts that become an Internal Problem for one or both of them.
It’s not always necessary for the Heroine and Hero to both have a secret/internal issue. Sometimes it’s just one or the other. In Twilight, Bella is a normal girl; Edward has a secret. But in the subplot romance of Bella and Jacob, both Bella and Jacob have an internal issue. Jacob has a secret identity. Bella’s issue is that she’s still in love with Edward. In the Bella/Edward romance, they are able to overcome their external and internal problems, whereas Bella/Jacob are not. (Obviously the Bella/Jacob love story could not stand alone and still have the required HEA, but as a subplot, it works. Romances can have bittersweet, unhappy for now, or even unhappily ever after subplots for the third wheel. Usually, though a HEA is implied even for the loser of a love triangle, unless the rival was a Baddie.)
This Grid is solely for Obligatory Scenes. It could easily be expanded along the y-axis to include all the beats of a standard Narrative Arc. Several of the Obligatory Scenes are also usually broken up into successive scenes in a standard length novel.
The First Kiss can be extended into a sequence in either direction: The First Look, the First Touch, the First Time to First Base, the First Time Making Love, the Second Time Making Love…and so on. In Romantic Erotica, the first sex scene might occur about two seconds after the Cute Meet. A Sweet Romance might replace the First Kiss scene with a gentle holding-hands gesture, and the couple might not kiss until the final scene when the preacher says: “You may kiss the bride!”
A Romance trilogy that follows the same couple may extend the later beats, such as Kiss, Fight, Commitment and Betrayal, several times, with a new arc in each book. The true HEA is withheld until the last book in the series.